We saw the legendary Keith Morris play with his band OFF! (formerly the frontman of Black Flag and Circle Jerks) a few months ago, right before the 2024 U.S. election. In between songs, speaking to a mesmerized New York packed crowd, he ranted repeatedly, “We think we have a choice, we think we have a choice, we think we have a choice…”
This stuck with me. At the surface, we have tons of choices, but who is steering these choices, and are we siphoned into just a handful of 1-2 choices when it comes time to who we vote for, what social media platforms we participate in (bye bye TikTok), or what food choices we have on hand? We live in a monopolized, concentrated, and consolidated world order with massive power imbalances.
Now, dear reader, I am well aware that I live in a country with technically endless choices, and democracy is technically still standing (some would disagree with that!). Choice can be a beautiful thing. The choice to celebrate. The choice to act. The choice to revolt! The choice to check out. However, cracks are emerging across many countries and communities, beckoning questions like who has more choice? Who has less and why? Who is steering our choices? Who is interfering with them?
Yet, I wonder more and more about equity, freedoms, and diversity of choice, particularly in the context of food systems, and how these systems fundamentally are meant to ensure food security and optimal nutrition.
Equity of choice
The diversity and range of food choices depend on who you are, where you live, and the structures that support your life. The ability to choose a nutritious diet is conditioned by inequities in food access—which stem from broader social inequities. For example, physical, economic, and social access to food can provide many or limited choices. Consider these questions:
How close do you live to food sources?
Are you living in an area that lacks affordable, healthy food?
Do you have to take two buses and a subway to get to the market?
Do you need a car because there is no public transport?
Once you get to the market, can you afford the food?
Do you have enough money to buy food?
Are the markets even appropriate to your social norms and culture?
Do systems oppress your ability to choose?
And that's just for consumers! Think about farmers: Can small-scale farms and enterprises compete with large farms or transnational companies, or do they have to make harder, more limited choices to stay competitive?
Freedom of choice
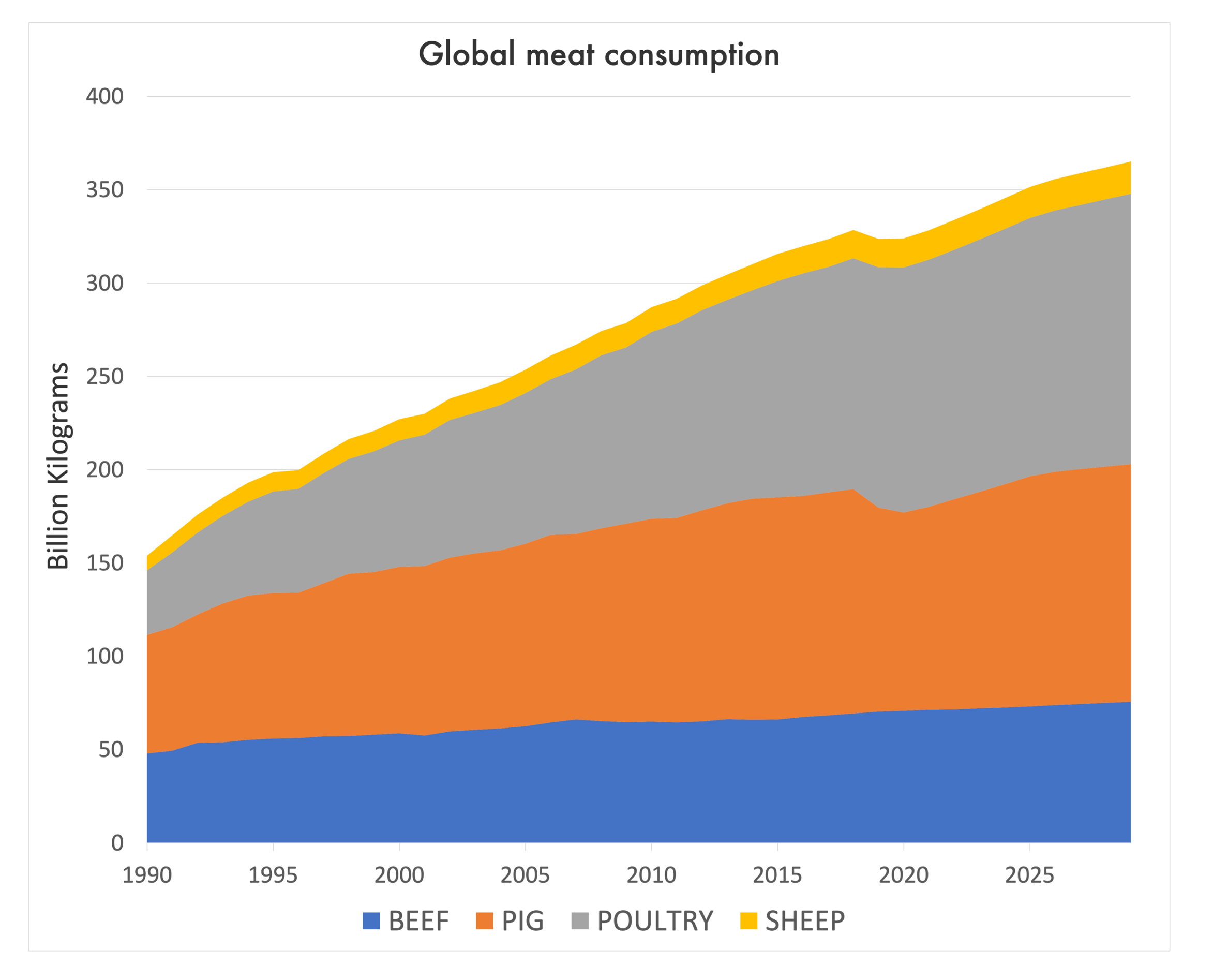
Those who have the freedom of choice — in what kinds of foods they eat, how much they eat, and for farmers, what they grow and how they grow it — can make choices that benefit the world. For example, if countries with high meat consumption reduce their intake, they could help mitigate climate change, improve environmental sustainability, and promote animal welfare. It is often thought that one person can't change the world. Yet, we know that individual actions, when combined, can lead to collective impact. Individual choices can create change.
But people want autonomy. They don't want to be told what to eat. And they don't always want to make choices based on altruism. Many resonate with Federico Fellini, who once said...
"I became burdened…with useless baggage that I now want off my back. I want to uneducate myself of…worthless concepts, so that I may return to a virginal personality…to a rebirth of real intent and of real self. Then I won’t be lost in a collective whole that fits nobody because it’s made to fit everybody. Wherever I go, from the corner of my eye, I see…people moving in groups, like schools of fish… This is one of the things I fear more than anything else. I loathe collectivity."
That may be true. In the United States, for example, dietary choice is often driven by taste, price, and convenience and is less about solving “we are all in this together” problems such as climate change.
Diversity of choice
While some have more freedoms when it comes to choice, it begs the question as to how many choices we have within choice. Do we have a lot of variety, diversity, and range of choice? Some would argue no because the world has become more similar and homogeneous. We are converging. Technology has helped with process along. As Herbert Marcuse argued in his book One Dimensional Man, while technology provides endless information and choice, it would result in less variety of ideas and creative thinking. So, although people think they have more choices, the choices lack significant differences. This was written in the 1960s…
When considering the diversity of choice, it raises the question of who provides it. We know that our global food system is hyper-consolidated and concentrated — from the seeds to the inputs used on crops, to the varieties of crops grown and the agricultural subsidies that support only a handful of crops, to the retail markets that sell us our food. A handful of transnational companies control the majority of supplies, commodities, and foods we eat at every step of the supply chain.
Just knowing this makes me want to pull a Lloyd Dobler. If you don't know who Lloyd is, I encourage you to watch "Say Anything" — an '80s romantic comedy written and directed by Cameron Crowe. The lovable Lloyd Dobler, played by John Cusack, is asked about his plans for the future. He says:
I don't want to sell anything, buy anything, or process anything as a career. I don't want to sell anything bought or processed, or buy anything sold or processed, or process anything sold, bought, or processed, or repair anything sold, bought, or processed.
That sounds about right. You might want to avoid products made, processed, or sold by massive corporate food companies, but here's the harsh reality: we often don't have a real alternative. The scary part? Many of us can't simply opt-out. We can't all plant our own gardens, eat exclusively from what we grow, show local, and choose only foods that are good for us and the planet. The food system is like an invisible cage, constraining both farmers and consumers. Our choices are frequently predetermined by complex, interconnected systems that prioritize efficiency and profit over individual well-being and environmental sustainability. It's not just about willpower or desire. The barriers are systemic, making truly independent food choices incredibly challenging for most people. We're caught in a web of limited options, corporate control, and economic constraints that make genuine food autonomy feel like an impossible dream.
But I have hope on this holiday, Martin Luther King Day (yes, I am ignoring that other big event). He said, “There are a lot of things you can't choose for yourself, but you have to keep moving forward.” And we will do just that.