FOOD BYTES IS A (ALMOST) MONTHLY BLOG POST OF “NIBBLES” ON ALL THINGS CLIMATE, FOOD, NUTRITION SCIENCE, POLICY, AND CULTURE.
I am here in Gotham City, writing my final blog post for 2024 in the quiet. This is one of my favorite times of the year. Not because it is Christmas and New Year’s, but more so because the whole world pauses. Less email, less bustle, less stress. The opportunity to not have to click on that Zoom link for a week or two is just pure bliss. My posts as of late have gone from reflection to angst to dread, but at this moment, dear reader, I am feeling “set” — like a voluminous beehive hairdo or a delightful buttery pound cake. I am ready to take on whatever 2025 brings, as I hope you are.
This is my last Food Bytes of 2024. I managed to publish 9 (not 12) this year. I learn a ton gathering up material for the monthly Food Bytes as it forces me to do some reading, listening, and watching to highlight the prolific content being put out in the world on food systems, climate, and nutrition. I feel incredibly fortunate to work in an area so rich and doused with science, politics, culture, and controversy. This area of chosen work would be dull without those elements all jumbled together and needing constant teasing apart. So here it goes…my last Food Bytes of 2024. Hang onto your hats, guys and gals, for a very interesting 2025…
Let’s start with obesity. There is so much coming out related to obesity prevalence and trends, as well as the new GLP-1 anti-obesity class of medications (formally known as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists). Earlier this year, the NCD Risk Factor Collaborators published a paper in the Lancet showing the obesity and undernutrition trends among adults and children. They showed that we have moved from a world paralyzed by undernutrition to a world of obesity, with some countries struggling with both forms. One in 8 people are obese - or 1 billion people suffer. Many of you know this story of the nutrition transition and the double and triple burdens of malnutrition, but the overall picture over the last 30 years is quite staggering. Check out the circular bar plots of the changes in the underweight burden (the blue bar's length shows prevalence) and obesity (pink/red bar) among women in 1990 and 2022.
Another paper just released, again in the Lancet, showed in the United States, between 1990 and 2021, the percentage change in the prevalence of obesity in adults was 123.6% in men and 99.% in women. They forecast that by 2050 if current trends continue, the total number of adults with overweight and obesity will reach 213 million. And I am not even reporting on teen prevalence. Wowsa. Yet, JAMA just published results that found that the prevalence of BMI and obesity in the United States decreased in 2023 for the first time in over a decade. Some pontificate it is because of the GLP1 inhibitors, others because of COVID-related deaths (obesity being a heightened risk factor for morbidity and mortality associated with COVID).
The difference could be that the Lancet paper by the Global Burden of Disease 2021 US Obesity Forecasting Collaborators didn’t investigate trends beyond 2021. In contrast, the JAMA authors showed a decline in 2023 specifically. Also, we don’t know the future of the GLP-1s. Currently, they are cost-prohibitive for many living in the United States and, moreover, the world. One report estimated that if half of U.S. adults with obesity took these drugs, it could cost the healthcare system $411 billion per year. The inequities in who has access to these drugs are staggering.
These medications certainly help people lose weight, with various studies showing reductions in body weight somewhere between 10-25%, as well as other benefits for those struggling with diabetes and cardiovascular disease, to name a few. I worry that we still know so little about obesity, its drivers, and the potential ramifications of medicalizing the challenge into one silver-bullet solution. I also fear that the scale-up of these drugs gets food systems and industry “off the hook.” Why stop making ultra-processed foods and ensuring food environments are healthy for people when they can easily take these drugs? But RFK Jr is going to solve all that, right? Don’t hold your breath. I appreciated this commentary by Francesca Celletti and colleagues in JAMA on where we are at in our understanding of obesity:
“The seriousness of the crisis is now widely recognized. Yet there are many challenges that continue to hinder a successful national and global response. Perceptions and attitudes toward obesity, including the debate about whether obesity represents a risk factor or a disease, are widely divergent. Efforts to address the stigma associated with obesity have, in some cases, evolved into a narrative that obscures the importance of obesity-related morbidity and mortality. Compared with other noncommunicable diseases, there remains a lack of knowledge on the associated biological and genetic factors, and there are inconsistencies in the appreciation of the effect of obesity on other noncommunicable diseases and the overall burden of disease. There is limited evidence on long-term management interventions and their effectiveness among populations most at risk and in low-income settings in relation to issues such as access and adherence.”
Speaking of nutrition trends, the Global Burden of Disease Group published their analysis on global, regional, and national progress towards achieving the six nutrition-related Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) targets by 2030. The picture ain’t so rosy. These are their high-level results: “In 2030, we project that 94 countries will meet one of the six targets, 21 countries will meet two targets, and 89 countries will not meet any targets. We project that seven countries will meet the target for exclusive breastfeeding, 28 for child stunting, and 101 for child wasting, and no countries will meet the targets for low birthweight, child overweight, and anaemia.” Looking at current trends, the authors show that in 2021, seven countries had already met two of six targets (Georgia, Mongolia, South Korea, Peru, Rwanda, American Samoa, and Puerto Rico). What are they doing right? Case studies, anyone?
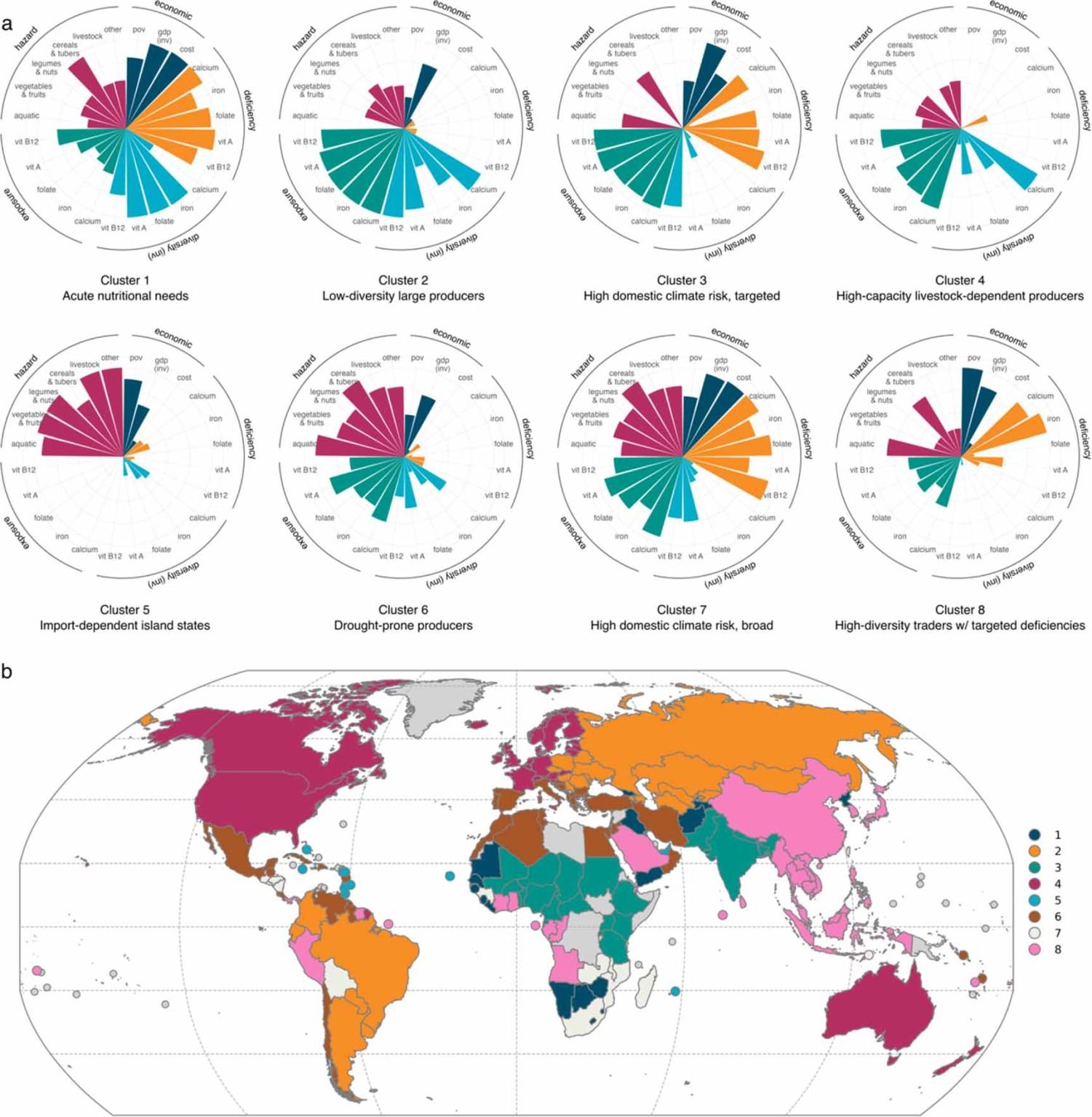
Diets heavily weigh into dietary outcomes, and as the SDGs stand, there is no target or monitoring of a dietary indicator, such as dietary diversity. SDGs. One of the juggernauts of our diets is how much animal source foods we should or could consume that benefit our health and the planet. A PNAS special feature delves into this quandary in what I think is quite a balanced set of papers showing all the angles and issues. We contributed a piece laying out the biological nutritional vulnerabilities stemming from high micronutrient needs per calorie among infants and young children, women of reproductive age, pregnant and lactating women, and older adults, particularly older women, and the importance of nutrient-dense foods coming from both plant and animal-source foods. Speaking of nutrient-dense foods, some colleagues from the Blue Foods Assessment published a paper in the Environmental Research Letters that assessed nutrition-sensitive climate risk to five essential micronutrients across production systems. By mid-century (2041–2060), we estimate that 75% of calcium, 30% of folate, 39% of iron, 68% of vitamin A, and 79% of vitamin B12 produced in primary food products will face frequent climate extremes globally. Nearly 50 countries are projected to face high domestic climate risk for two or more micronutrients during this period. Check out the figure below.
Speaking of the climate crisis, I have written before about tipping points, but some scientists argue the framing is distracting and confusing. Regardless, people are fatigued and confused by all the terminology: diebacks, atmospheric rivers, bomb cyclones. Grist calls it “alert fatigue”. The question is, does the fatigue translate into inaction? The scientists in that Nature paper argue that urgency and the terms and definitions to illustrate that urgency do not always translate into political commitments. And sadly, people are being left behind. Did you hear about Cyclone Chido on the French island of Mayotte? Neither did I. People are dying from climate-related extreme events, and we aren’t even able to count the dead or notice. Unless you live in a rich country… We are really on the edge here, and leaders seem to be shrugging their shoulders. Look at this year’s various COP events - climate, biodiversity, and dry lands. Were any binding and bold commitments made? Nope. And science is under ever more scrutiny and openly ignored and disregarded by some. This title says it all: Good COP, Bad COP, science struggles under a year of environmental summits. As this editorial argues in the Lancet Planetary Health, somebody has to move first. As the editors wrote: “…The absence of consensus on the world stage should not hold back individual countries from moving rapidly away from fossil fuels and benefitting from this. Keeping warming below 2°C is still possible, and actions that limit warming to almost any degree will be beneficial, but some have to do the right thing and decisively move first.” The question is, who will be brave enough?
But we scientists keep churning. The IPBES Nexus and Transformative Change assessment summary reports have been released (my hermano, Mario Herrero, one of the lead authors says the very long reports are coming soon). First, what is IPBES? It is the Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. It is similar to the IPCC in that it sits at the interface between science and policy and is meant to spur evidence-based political action. The Nexus report argues that we need to holistically tackle biodiversity loss, water and food insecurity, health risks, and climate change because these five areas interact, cascade, and compound each other, and addressing them separately is counterproductive, redundant, and inefficient. The Transformative report focuses on the underlying causes of the biodiversity crisis, the drivers of change, and available options and argues for a “whole of society” approach. Overall, their analysis is not a chipper one. Half of the world lives in areas hit hard by food and water insecurity and biodiversity loss. Biodiversity is in massive decline. And delaying action will be catastrophic. Action in these areas could unlock trillions of dollars in economic growth and jobs. The figure below is worth a lot. It shows a wheel of interconnected challenges (different colors) and barriers (different 637 letters) to transformative change.
We continue to push out sound data to inform policymakers across food systems. The Food Systems Countdown to 2030 Initiative will publish its 3rd annual paper in January, so stay tuned for that. Meanwhile, a few of us at the Columbia Climate School wrote a piece for IFPRI’s Impact group on food system data gaps and the future potential to measure food systems data with new big data technology.
As you may know, I am a big fan of rivers. This poem, Rest, Like a River by Leena Danawala is a fitting way to close out 2024:
I like the idea of a river yawning:
its mouth a vast open width,
just a symptom of fatigue.
I think of how it wraps its length
around itself, serpentine and sure;
how its waves rock back and forth,
a cradle on an unsteady floor.
on days like today, when the
spring fog has melted into my bones,
or when time seems to stop or slow,
I think of my spine as that river
and curl into myself like the letter “c.”
breath floating downstream,
body swaying like the currents of the sea.