FOOD BYTES IS A (ALMOST) MONTHLY BLOG POST OF “NIBBLES” ON ALL THINGS CLIMATE, FOOD, NUTRITION SCIENCE, POLICY, AND CULTURE.
The chaos of the semester has begun along with the long lead-up to climate week here in NYC. Many side events are happening around the UN General Assembly (UNGA) and Climate Week. Do all these events amount to something tangible? It is unclear in my mind’s eye, but I do love seeing food experts and friends converge in Gotham.
So let’s get started. If you are coming to NYC next week, please do join us at Columbia for the Bollinger Convening, where we will highlight the importance of evidence, research, and data (although you wouldn’t believe they matter if you watched the U.S. presidential debate - cats? dogs?) in addressing hunger and malnutrition. We are also hosting a Forward Food & Fashion event. Join us!
So first, the most depressing. Sudan’s famine situation is worsening to a catastrophic level. Absolutely devastating. Let’s hope this is high on the agenda at the UNGA and that leaders act swiftly. While some argue that Gaza is also experiencing a catastrophic famine, others disagree — the debate played out in the American Journal of Nutrition. Michael Fakhri, the Special Rapporteur on the Right to Food, also weighed in.
Some papers I am reading this week:
Simone Passarelli and colleagues performed a modeling exercise to estimate micronutrient intake and adequacy worldwide. They found that 5 billion people do not consume enough iodine (so much for iodized salt!), vitamin E, and calcium. At least half of the world does not consume enough folate, iron, and vitamin C. We still have a long way to go to ensure people get access to nutrient-dense food products.
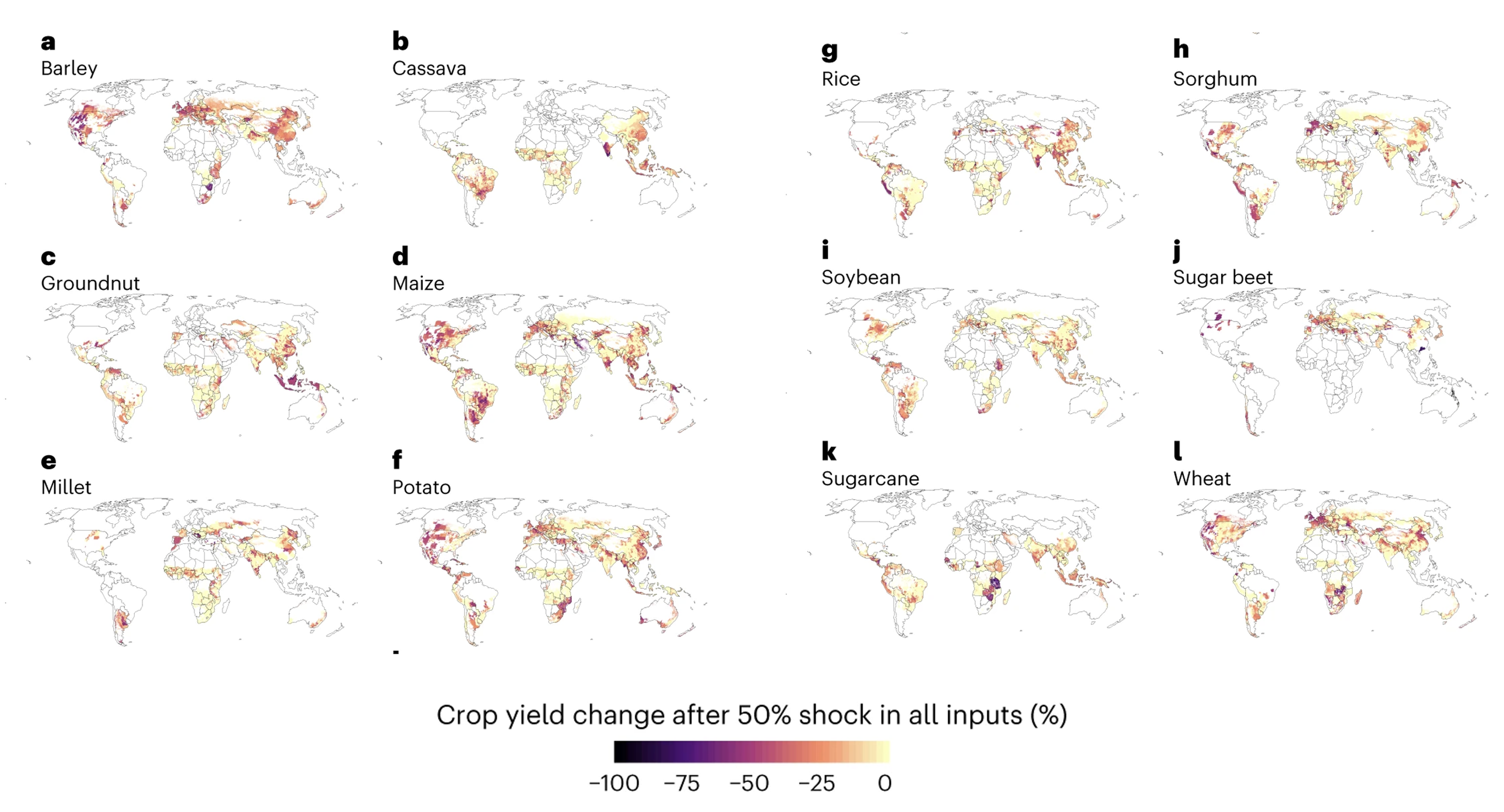
Yi Yang and colleagues recently published a paper in Science on how climate change could amplify the environmental impacts of agriculture. They found that not only will it do so, but it will also reduce the efficacy of agrochemicals and their loss into ecosystems and increase soil erosion and pests. This will reduce productivity, leading to land expansion and clearing to grow more food inefficiently, threatening biodiversity and accelerating greenhouse gas emissions and pollution. They nicely demonstrate the interconnected feedback loops.
Speaking of climate change and Science magazine, a fascinating article examining climate policies that achieved significant greenhouse gas emission reductions. What an undertaking. Between 1998 and 2022, they examined 1500 climate policies across 41 countries. They found 63 successful policy interventions that reduced emissions between 0.6 billion and 1.8 billion metric tonnes of CO2. It is a shame they did not examine agri-food policies. Pricing, regulation, and subsidies had different impacts across sectors, but bundling of policy interventions greatly mattered. Important lessons for food-climate policy.
A new study in Lancet analyzed dietary questionnaires from more than 200,000 adults in the United States to examine their consumption of ultra-processed foods and related it to their chance of developing cardiovascular disease. They found that those who consumed the most ultra-processed foods were 11% more likely to develop cardiovascular disease and 16% more likely to develop coronary heart disease compared to those who consumed the least amount of ultra-processed foods. Which foods were the worst offenders? Sugar-sweetened beverages and processed meat, poultry, and fish (e.g. bacon, hot dogs, breaded fish products). But still, some worry that demonizing foods can be stigmatizing.
I am totally biased here, but my colleague Shauna Downs just published a paper in Appetite that examined meat (red, unprocessed, and poultry) and seafood consumption patterns, the factors influencing their consumption, and how these differed based on socioeconomic variables among a US population. One interesting finding is that critical factors influencing red meat reduction were health and price, while environmental sustainability and animal welfare were less important, particularly among certain socio-demographic groups. She also wrote this piece on how communities along the Mekong River in Cambodia are seeing their food access shrink as the climate worsens.
Other nibbles:
Did you know methane is getting rising faster than ever? No wonder with the massive demand for meat.
The European Food Trails project just released a Food in Cities podcast in collaboration with Slow Food. I'm looking forward to listening.
Speaking of podcasts, we at the Columbia Climate School’s Food for Humanity Initiative are starting our own podcast, the Food Pod for Humanity. It will be a limited series on topics highlighting the interdependencies of climate change and food systems. The first series is on food waste.
Speaking of Columbia’s Climate School, check out this inspirational story about one of our new students from South Sudan.
World Wildlife Fund’s new Great Food Puzzle interactive site is pretty awesome.
The Atlantic published a report saying that we are a country of snacking, and less on eating wholesome meals. Gee, I wonder who encouraged that?
And just on a personal note, I have always loved These Days by Jackson Browne. I was so happy to see the NYT highlight the song. As I age, lyrics like this just hit me right in the gut: “Don’t confront me with my failures/I have not forgotten them.” Beautiful, and written when he was just 16.