Rivers are special. These ribbon-like bodies of water cut through topography, shaping and shifting the landscape around them.
rivers begin where they end
if 1 considers rain + jet stream winds
look deeper into grainy sands
the sublimation from the wind-swept lands ever reach sea — Jordan, Sound Furies
My partner and I have always been drawn to rivers and try to live or be near them. We currently reside quite close to the great Hudson River (~500 km long), where we can amble through Riverside Park and enjoy the views. We are so obsessed with rivers that we made a double album as the Sound Furies dedicated to rivers, entitled “Tributaries.” One of my favorite songs from the album is Columbia.
We are not alone in our obsession with all things river. There are many songs inspired by rivers in the archives of rock-n-roll. Al Green just wanted someone to take him to the river. Jimmy Cliff had many rivers to cross. Joni Mitchell longed to have a river to skate away on. Sam Cooke was born by a river. Tina fearlessly rolled on a river (thanks for the original CCR). I could go on and on, but I think you get the point. Rivers mean something to many of us.
It is not just music. There are a plethora of movies about rivers. African Queen, A River Runs Through It, and one of the best movies ever made which spends most of its time on the river, Apocalypse Now. In the movie, the French woman living on the plantation says to Willard (played by Martin Sheen), “Do you know why you can never step into the same river twice?” Willard answers, “Yeah, 'cause it's always moving.” The best scene, though, is the conversation between Willard, who has come to assassinate the unhinged Colonel Kurtz (played by Brando). They converse about the Ohio river and a gardenia plantation.
What was up with all those movies in the 90s about dead bodies being found along river banks — Short Cuts, Stand By Me, A River’s Edge, and of course, David Lynch’s Twin Peaks? We Gen Xers were so demented.
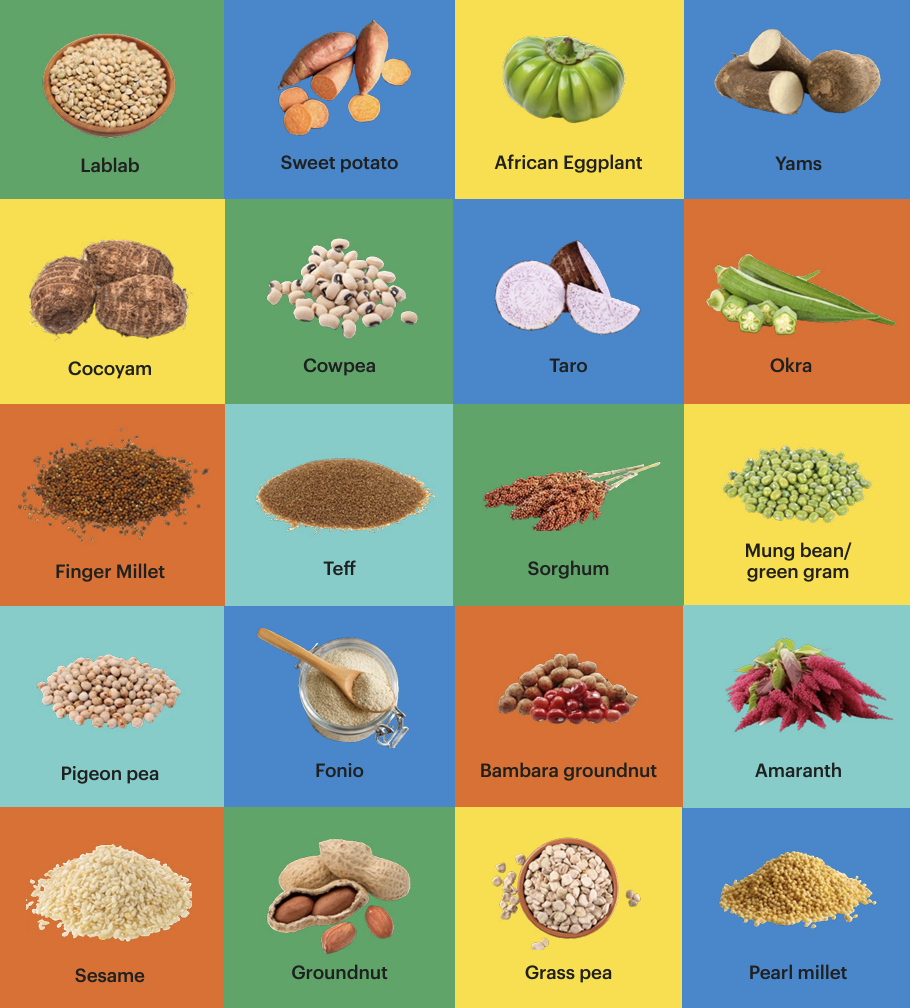
Supposedly, there are 165 major rivers around the world, but no one really knows the real number. The five longest rivers in the world are the Nile, which starts in Uganda and moves north (odd, right?) to Egypt, the Amazon-Ucayali-Apurimac in South America, the Mississippi-Missouri-Red Rock in the U.S., the Yangtze in China, and the Yenisey-Baikal-Selenga in northern Asia. The Nile is the longest, topping out at 6,650 km. The Danube in Europe flows through 10 countries. The Congo River is the deepest. Rivers serve all sorts of purposes. They provide water, food, habitats, transportation, and recreation, to name just a few purposes. Rivers are really important for food. Fish and other aquatic creatures that live in rivers are consumed. Food is traded on and transported by rivers. Food is grown in or around river banks. Water from rivers irrigates crops.
We wrote a paper on the dynamism and multifaceted nature of rivers as food environments (i.e., the place within food systems where people obtain their food) and their role in securing food security, including improved diets and overall health. In the figure below, we showed the elements of multidimensional riverine food environments.
The paper nicely describes why river ecosystems are so critical. “Rivers can be described as nutrient highways across the earth’s surface, transporting sediment and water, sequestering carbon from the atmosphere, and connecting and storing immense biodiversity through aquatic life. The flow and transportation of sediment create environments for cultivation (e.g. rice farming), with river deltas being one of the world’s most agriculturally productive areas. Rivers support approximately 1/3 of all global food production, and an estimated 70% of freshwater from rivers is used for agriculture.”
There are so many challenges with rivers. The first issue is environmental: climate change, environmental degradation, and pollution are vastly changing these waterscapes - altering their composition and flow. The second issue is overfishing and overallocation, meaning the building of dams for electricity, are altering the riverine ecosystems and marine life and creating water shortages and river connectivity, respectively. As for rivers that cut across multiple countries, who governs these waters and decides who can build dams and where? We see those challenges in large rivers such as the Mekong — where China is building dams upstream impacting many Cambodian and Vietnamese living downstream. We also see this with the Nile, in which Ethiopia is building damns to electrify the nation, which could have massive impacts on irrigation systems for Egyptian agriculture. The third issue is that while rivers transport and contain food, they also bring other things, like diseases and unhealthy foods deep into river communities. This New York Times article discusses how the Amazong brought the COVID-19 pandemic into the far reaches of the Amazon forest.
The spread of covid in just a few months during the pandemic along the Amazon waterways. Source: NYT
“The Amazon River is South America’s essential life source, a glittering superhighway that cuts through the continent. It is the central artery in a vast network of tributaries that sustains some 30 million people across eight countries, moving supplies, people and industry deep into forested regions often untouched by road. But once again, in a painful echo of history, it is also bringing disease.”
The Amazon also carries highly processed foods. According to this article, multinational companies like Nestle had river barges that delivered junk foods to isolated communities in the Amazon basin.
There is also the issue of rivers flooding, damaging infrastructure and harming humans and animals in their way. And now, we are experiencing rivers above us — atomospheric rivers — corridors of concentrated water vapor in the atmosphere that wreak havoc. What the hell?!
World WildLife Fund’s solutions for sustainable rivers
I can’t recommend enough the documentary “A River’s Last Chance,” about the Eel River. It delves into the history of how this river has been managed, or lack thereof. The Eel River is in Northern California and has been vulnerable to overfishing of its salmon, logging, floods, droughts, and dams. While the wild salmon population is trying to recover, new cash crops—weed and wine — threaten the salmon once more. It is quite a story of a river struggling to survive.
World Wildlife Fund has a fantastic initiative, Rivers of Food, in which they propose a four-pronged solution towards a more sustainable future for rivers and food security.
Let’s hope rivers can be saved as they provide a vital lifeline for nature, animals, and humans. They are also just so romantic and atmospheric. We used to dwell right near the Tiber when we lived in Rome. It was so magical. The way the early morning light hit the surface of the water, the banks, and the bridges. During the late summer months of the year, the starlings would circle around the Tiber, before settling in for the night in the treetops along the river banks. In Paolo Sorrentino’s La Grande Belleza, the early morning light on the Tiber is captured so beautifully below.